Bridging the gap between energy efficiency and fire safety: a Q&A blog
Through our recent partnership with Technoform we’ve developed a new fire-rated solution, with the use of high-performance warm edge spacers now available ‘as standard’ in many of our IGU constructions.
In this blog, we chat with Richard John, Technoform’s Product & Market Manager UK & IRE, and Andy Lake, our UK & IRE Sales Director, to find out how it all came about…
Q) Why is sustainability and energy efficiency so important for the glazing industry?
Andy: Sustainability is a topic that is hitting all industries hard. It can take many forms, whether that’s sourcing responsible materials, reducing the embodied carbon in new buildings during construction, working to lessen the operational carbon or recycling materials at their end of life.
The energy efficiency of glazing systems is just one way in which we can build the greener buildings of our future, helping to reduce the energy needed to heat or cool the interior space and cut costs as a result.
Richard: In many ways, the glazing industry has been overlooked for too long when it comes to energy efficiency, perhaps due to the historical poor thermal performance compared to other structural elements. For example, if we look at Approved Document L of the Building Regulations, it talks a lot about the roof, walls and floors of a building but less so about the glazing.
However, this is all beginning to change, with glazing systems in new buildings and refurbishments expected to deliver lower and lower U-values. This demand is coming from the top and U-values are being referred to more, increasingly looking at the building as a whole system, and the glazing industry has a clear role to play within this.
Q) Why are the original spacers commonly used in fire safety glass systems not so great from an energy efficiency perspective?
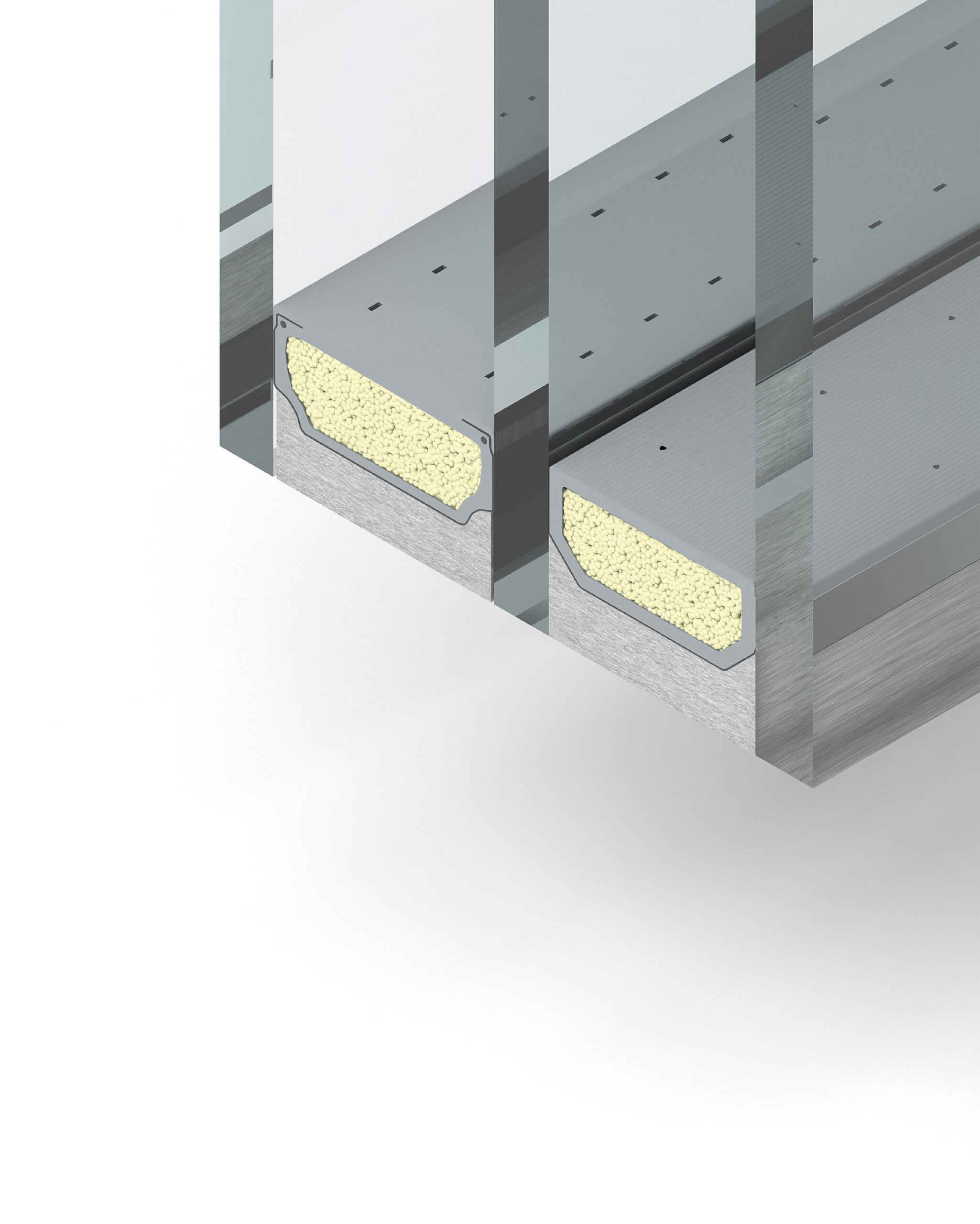
Richard: It’s all based on U-values, also known as thermal transmittance. It’s a way of measuring and comparing the rate of transfer of heat through a structure or material. ‘Standard spacers’ that are used in many fire safety glass systems are often manufactured from metal (a conductive material) to the detriment of thermal performance. Whereas warm edge spacers can help to control this thermal bridging, driving down U-values.
Andy: Yes, for example, if we look at a fire-rated IGU, the glass itself could have a U-value of 1 W/m2K. However, if you were to use a typical spacer, this could impair the U-value and energy efficiency of the overall glass system, increasing the U-value to 1.2 W/m2k.
We need to look at how we can drive down those U-values in fire-rated systems, all without any drastic or significant changes to the system or its construction.
Q) What does Technoform specialise in?
Richard: We’re specialists in insulation solutions for glazing and construction thermal bridging and have a wide range of precision engineered extruded polypropylene products and systems on offer. Our warm edge solutions set new standards in surface quality and match the highest requirements of architects and building owners. Its hybrid warm edge spacers achieve excellent thermal performance without sacrificing design and, most importantly, durability.
Q) How did the collaboration between Pyroguard and Technoform come about?
Richard: It was a couple of years ago and completely by chance that I first met Vince Crook, Pyroguard’s Technical Development Director, and the conversation really went from there. After sitting down and discussing some initial ideas, we then developed these further and carried out a series of full-scale fire tests under UCAS accreditation.
The issue here is that some non-fire rated warm edge spacers are manufactured from carbon fibre or other similar materials, a construction that just wouldn’t work in a fire safety glass system. So, you therefore need a material that will remain strong and structurally stable in the event of a fire, such as stainless steel.
Andy: It took us some 18 months to complete the test programme that followed, but we were able to achieve outstanding results with Technoform’s SP 14 warm edge spacer for both 60- and 90-minute fire classifications.
Q) Can you tell us more about the newly tested warm edge spacer and its construction?
Richard: While fire-rated spacers are commonly manufactured from metal, our Technoform SP14 spacer has a unique hybrid construction of precision engineered polypropylene and steel. The SP14 delivers improved thermal properties, while the inclusion of steel co-extruded into the spacer structure offers structural stability and durability in fire situations.
Compliant with BS EN 1364, as well as CE and UKCA approved, this warm edge spacer is available in widths from 8-32mm.
Q) What are the benefits for architects, contractors and fabricators?
Richard: Ultimately, it’s about proving that you don’t need to compromise on energy efficiency in order to meet safety and fire safety standards. It’s no secret that the construction industry continues to be affected by the Grenfell Disaster of 2017, and this will continue for many years to come. It has been a big driver in terms of encouraging and bringing about change and improved fire safety standards for buildings. Yet why are we constructing safer buildings but not considering thermal bridging?
Andy: This is one of the reasons why we chose to offer the new warm edge spacer as standard across a range of Pyroguard’s IGUs, as opposed to being positioned as an upgrade or value-added option. This was really important for us as a means of driving change for the glazing industry and demonstrating that technology like this really should be the norm.
It should be expected that you are to construct green and safe buildings, and this new warm edge spacer is a great example of this in practice.
For more information, please contact us.
